Improving Efficiency in Passive Infrared Sensor Applications
Passive infrared (PIR) sensors are almost always used to detect whether a human has moved within the sensor’s range, but the simple triggering algorithms used are sensitive to other types of movement. High rates of false alarms are produced when the sensor is triggered by movement from unwanted subjects like pets and automobiles. Attempts to reduce these false alarms by lowering the sensitivity of the device often causes high rates of missed detections.
In this technical paper, “Power-Efficient Object Detection in PIR Data Using Syntiant NDPs,” findings reveal that when advanced AI algorithms are used to properly train deep neural networks, both false alarms and missed detections can be drastically reduced by 80 and 60 percent, respectively.
Download the paper below to learn more.
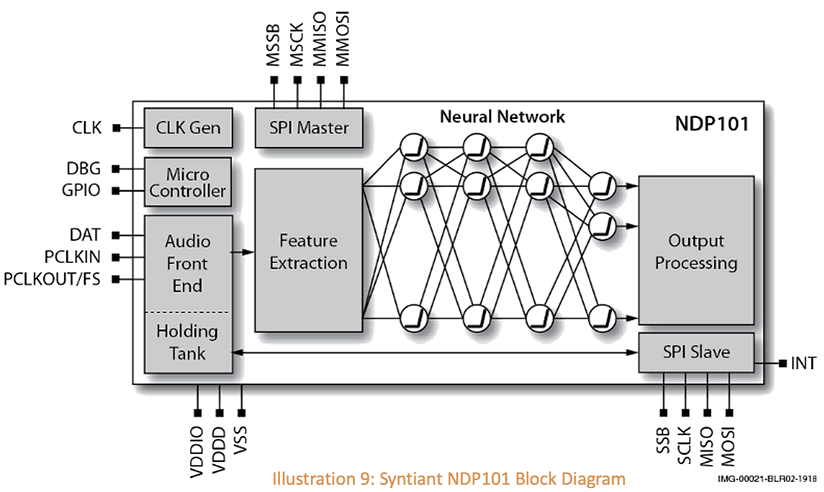
Syntiant’s Neural Decision Processors™ achieve approximately 100x efficiency improvement over stored program architectures such as CPUs and DSPs, and are easily programmed and integrated using Syntiant’s accompanying TDK and SDK.
For more information, contact us at info@syntiant.com.